GS’s 7 Reasons for a Crash
News
|
Posted 11/09/2017
|
6197
Goldman Sach’s chief equity strategist last week laid out his 7 main reasons why they are worried about this equities market. Here they are:
- 1. History. Many investors argue the bull market is “long in the tooth” and will soon come to an end. It has been 14 months since the S&P 500 index experienced a 5% sell-off and 19 months since the market had a correction of 10%. The last bear market defined as a fall in the index greater than 20% ended in 2009. The current bull market has lasted for 8.5 years and the S&P 500 has climbed by 260% compared with a 124% rise in earnings and a 64% P/E multiple expansion to 18x forward EPS.
- 2. Volatility (or lack thereof). Realized 3-month vol is nearly the lowest in 50 years. Implied vol as measured by the VIX stands at 12, a 6th percentile event since 1990. In his recent book, Tectonic Shifts in Financial Markets, the legendary Salomon Brothers economist Henry Kaufman (with the superb sobriquet “Dr. Doom”) references the lesson of Sherlock Holmes in “The curious incident of the dog in the night-time” that what doesn’t happen matters as much as what does. Low volatility across asset classes may be masking risks that are not evident today but will be obvious in retrospect.
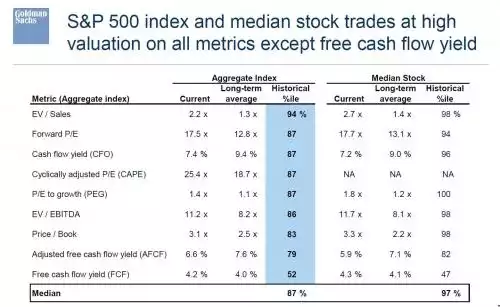
- 3. Valuation. Equity valuations are stretched on almost every metric. The typical stock trades at the 98th percentile and the overall index at the 87th percentile relative to the past 40 years. Only on a Free Cash Flow (FCF) yield basis is the market valued at an average level (4.4%). But as we detailed in a recent report, the collapse in capex spending explains the FCF yield. On a cash flow from operations basis the market trades at the 87th percentile. Other asset classes are also highly valued vs. history: nominal Treasury yields (92nd), real yields (75th), and HY (75th) and IG (69th) spreads.
- 4. Economics. The current US economic expansion just celebrated its 8th birthday making it one of the longest stretches without a recession. Only the 10-year expansion during 1991-2000 and the 9-year expansion from 1961 to 1969 had longer durations. The median length of the 16 expansions since 1921 has been 42 months. Along with the question about an equity correction, another frequent inquiry is “when will the next recession occur?” Our economists assign an 18% probability of a recession within 12 months.
- 5. Fed policy. The FOMC has lifted the funds rate by 100 bp since it started tightening in December 2015. During prior hiking cycles, equity P/E multiples typically fell but multiples have actually expanded during the past two years. Futures imply one hike by year-end 2018 vs. our economists’ estimate of five. The uncertain pace of further tightening is a cause of much investor anxiety.
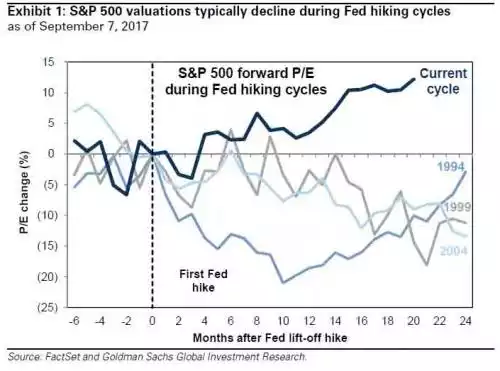
6. Interest rates. Two months ago, Treasury yields equaled 2.4%, ten-year implied inflation was 1.7%, and the S&P 500 stood at 2410. Our year-end forecasts of a 2.75% bond yield and a 2400 level in the S&P 500 looked rational. However, weaker-than-expected inflation data sparked a 35 bp drop in bond yields to 2.05% and a 2% stock market rally to 2465 (+10% YTD). Looking ahead, we maintain our year-end 2017 target (-3%).
- 7. Politics. President Trump’s fluid positions on domestic policy disputes in Washington, D.C. and geopolitical gamesmanship with Pyongyang and Beijing make political forecasting a precarious activity. One fund manager cited the “Law of Conservation of Volatility” under which there is a finite amount of uncertainty in the world. All the risk is now concentrated inside the Beltway and volatility outside of politics is close to zero. Of course, this could change at a moment’s notice.
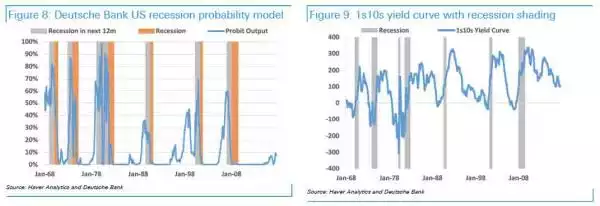
Just as a side note, that low probability they assign to a US recession looks a little shakey when you look at Deutsche Bank’s latest recession probability model below….