Ethereum 2.0 – What the Casper upgrade means for the market
News
|
Posted 26/11/2019
|
11505
Ethereum 2.0 (Casper) has been worked on for years and has undergone countless iterations. It's an extensive re-architecture of the Ethereum platform, involving new components such as proof of stake-based consensus, sharding (horizontal partitioning), a WebAssembly-based VM, and more. These changes, if successful, will provide vital boosts to Ethereum's security, scalability, and decentralization.
__________________________________________________________________________________
What is Proof-Of-Stake?
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a type of algorithm that determines distributed consensus in a cryptocurrency blockchain. In a PoS algorithm, users with the greatest stake in the system (e.g., age or wealth) are first to generate the next block and receive the network reward. PoS is an alternative to Proof-of-Work algorithms, in which users perform computational tasks to earn the right to create the next block.
PoS algorithms use randomization to create fairness in the block selection process. Without randomness, the system would not be decentralized at all, because the largest stakeholders would act as a centralized bank.
Each PoS algorithm may use its own combination of pseudo-randomness and stake to select which account will produce the next block. To prevent fraud, the tokens must be held in the account for a minimum amount of time before they can contribute.
Why move to Proof-Of-Stake?
One benefit of Casper is that, in making staking possible, it will help Ethereum become environmentally friendly. When it comes to electricity and computational resources, PoW-based systems are very onerous. In contrast, PoS models have a much lower demand. When a full PoS model is finally implemented in Ethereum, miners will no longer be needed to secure the blockchain, so the required resources and electricity costs will be much lower.
Another potential improvement of Casper is related to security. By nature, Casper will be used as a selector, responsible for ordering the chain of blocks. Basically, it will act as a bookkeeper of the Ethereum 2.0 ledger. So if a validator acts maliciously, they will be quickly removed and punished.
Casper will also give Ethereum more prominent levels of decentralization. For now, those who are most powerful on the network are those who have the resources to run mining operations. In the future, anyone who can buy a suitable amount of ether will be able to help secure its blockchain.
Together, developers of Ethereum hope that Casper will maximize energy efficiency, further support decentralization, allow for scalability and enhance economic security.
What this means for the Ether price
Where Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies at the time were primarily used as a store of value, Ethereum used computational objects called “smart contracts” to create code, upload it to the Ethereum blockchain, and then to run it.
Prior to this, the process for creating a cryptocurrency was typically either to copy or "fork" Bitcoin's code and make sparse modifications or to go through a lengthy and complicated process of creating fresh code from scratch.
Ethereum provided a fairly streamlined process where projects could quickly and easily design and implement cryptocurrencies, and this led to a surge of investment coming into the cryptocurrency market as it grew in size.
As well as creating entirely new cryptocurrencies, Ethereum also supported projects to create decentralized apps, or "DApps", and decentralized autonomous organizations, or "DAOs", both of which have had limited success compared to initial coin offerings ("ICOs").
The price of 1 ETH during the Ethereum ICO was $0.31 US, and with today's current value at almost $147 US (AUD $217) the ROI of investing in Ethereum over time sits at around 470x.
Over a period of 42 days, the Ethereum ICO raised over $18 million US which was the largest at that point in time and stunned many who were observing the crypto space.
Over the course of the second half of 2017, Ethereum would become one of the best performing cryptocurrencies by ROI, fed by the ongoing ICO boom and public interest focussing primarily on Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Since the inversion of 2018's bear market, and 2019's resurgence of crypto-assets, Ethereum has seen modest growth from $114 up to a current price of just under $217 – at one point going as high as $520.
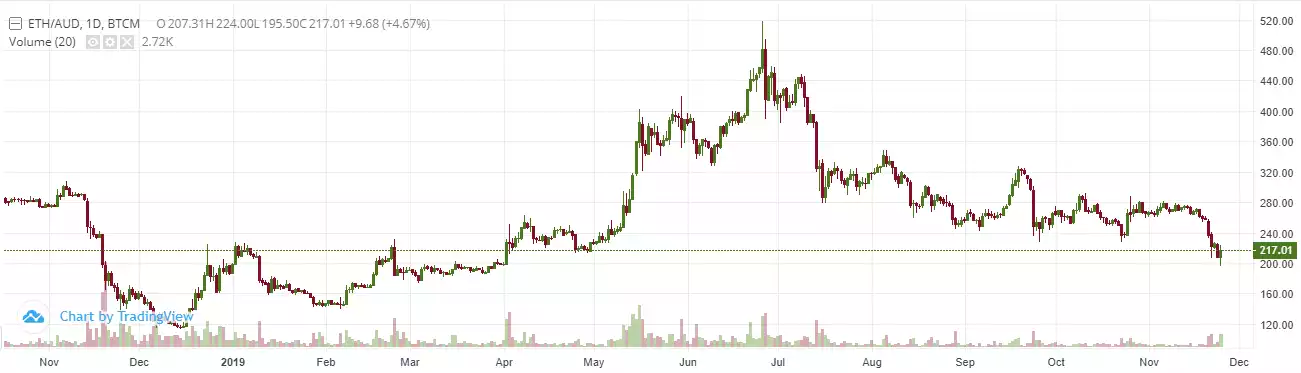
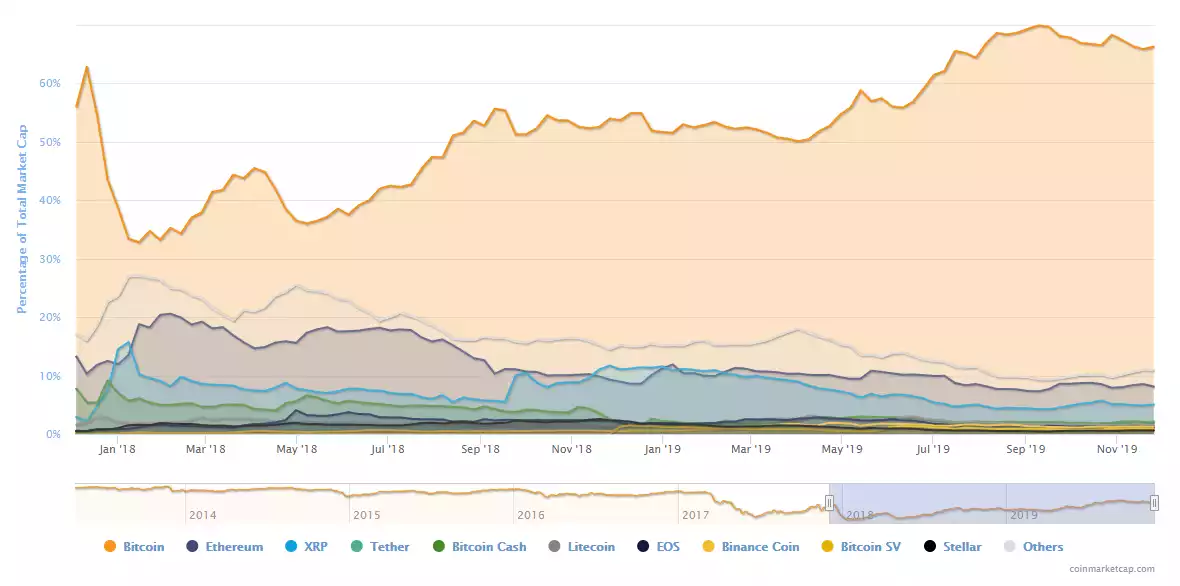
Although this growth is positive, Ethereum (and all altcoins in general) have not enjoyed the same levels of performance as Bitcoin in 2019, and this leads many to believe that throughout the end of this year or in 2020 an "altcoin boom" will be likely to occur. Bitcoin dominance has grown from 51.65% at the start of the year to 66.4% currently.
While Ethereum has been widely praised and has built a huge following from within the cryptocurrency industry, the project's core problem has been with the network's inability to deal with speed and scalability.
Throughout much of 2017, the huge influx of new users of cryptocurrencies and DApps sharing the bandwidth of the network revealed flaws in the system that were limiting Ethereum from effectively scaling to deal with higher throughput.
Instead of building these upgrades into the existing Ethereum system, Ethereum 2.0 is a separate system being built, which will replace the original system once the adaptations and testing are completed.
If the changes being implemented by Ethereum 2.0 are successful in mitigating the scaling and speed issues seen so far, there is a likelihood that as Ethereum's functionality improves, so will adoption, and therefore its value is likely to increase significantly.